Where can l use THHN wire?
THHN wire is a very common type of American standard wire with its unique characteristics, which gives it significant advantages in electrical and physical properties compared to traditional PVC insulated wires and cables. This article will give a detailed introduction to the common uses and structural characteristics of THHN wires, hoping that readers can better understand and apply wire products.

1. Application scenarios of THHN Wire
In commercial buildings, THHN cables are generally used for wiring electrical equipment such as distribution boards, lighting equipment, and air conditioning systems .
In industrial production lines, THHN lines are generally used to connect motors, control equipment and instruments .
In residential home environments, THHN cables are generally used for wiring sockets, switches and lighting fixtures.

2. Structural characteristics of THHN Wire
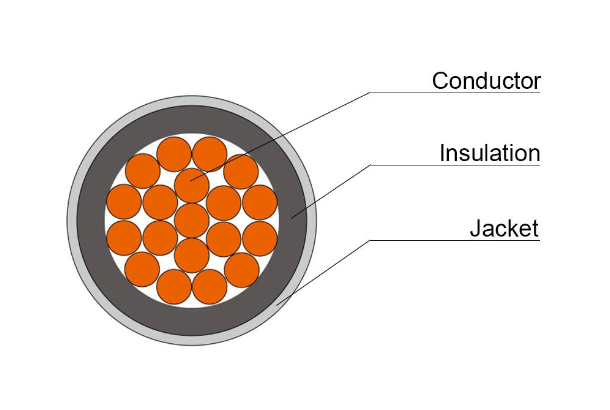
Conductor material: The conductor of THHN wire can be made of copper or aluminum. Since copper conductors have better conductivity and corrosion resistance, copper THHN wires are widely used in various electrical equipment and places. For example, copper conductor THHN wires are generally used for wiring inside some electronic equipment. If your budget is limited and you want to reduce costs, you can consider aluminum conductors, because aluminum conductors are cheaper and lighter. However, the performance is not as good as pure copper conductors, and it is more suitable for long-distance power transmission. For example, some power transmission lines in large factories use aluminum conductor THHN wires.
Insulation sheath: PVC insulation nylon sheath , PVC insulation has excellent heat resistance and electrical insulation performance, nylon sheath is resistant to high temperature, oil corrosion and good waterproof performance. This material can fully protect the conductor, thereby extending the service life of the wire. And when choosing wires, you can also choose the corresponding wire type according to the thickness of the insulation layer of the wire . For example, wires with thicker insulation layers can provide better electrical insulation performance . In high-voltage environments , THIHN wires with thick insulation layers are generally selected. Wires with thin insulation layers are more advantageous when space is limited, which is conducive to wiring. For example, THHN wires with thin insulation layers are generally used for wiring in small distribution boxes.
Rated voltage: The rated voltage of THHN wires is usually 600 V. This means that THHN wires can withstand voltages up to 600 V, so most low-voltage electrical systems can use this type of wire.
Rated temperature: The rated long-term operating temperature of THHN wire can reach 90℃ in dry environment and 75℃ in humid environment, and the minimum laying temperature is not less than 0℃. This shows that THHN wire can work normally at a maximum temperature of 90℃ and has high heat resistance. If some areas are hot and dry, the heating temperature is high, and the requirement for the cable must be heat resistance, this wire can be selected.
Flame retardant performance: THHN wires are available in flame retardant and non-flame retardant types. Flame retardant THHN wires are made of high-quality flame retardant materials, meet UL1581 VW-1 certification, have good flame retardant properties, and can prevent the spread of fire in the event of a fire. Therefore, flame retardant THHN wires must be used in some special places, such as crowded shopping malls and schools. Although non-flame retardant wires are relatively cheap, they have certain requirements for the use scenario.
Outer diameter size: From the perspective of cross-sectional area, THHN wires have a variety of specifications to choose from. Generally speaking, wires with smaller cross-sectional areas are more suitable for low-power electrical connections. For example, ordinary lamps generally use THIN wires with a cross-sectional area of 2.5 square millimeters. Wires with larger cross-sectional areas carry larger currents and are generally used for high-power equipment. For example, large motor starting circuits may require wires with a cross-sectional area of more than 10 square millimeters.
Color identification: In order to distinguish different circuits and functions, THHN wires use different color identification. Common color identifications include red, yellow, blue, green, etc. Common red THHN wires are generally used as live wires. Blue wires are generally used as neutral wires to facilitate the distinction of line functions. Yellow and green two-color wires are generally ground wires to ensure electrical safety. The combination of wires of different colors is also to facilitate installation and maintenance personnel to identify the lines.
Use environment: THHN wires are mainly suitable for dry and humid environments. If the wires are used in harsh environments with chemicals, such as the electrical lines of chemical plants, you need to choose THIIN wires with chemical corrosion resistance. Those wires with poor chemical corrosion resistance are only suitable for use in ordinary environments without chemical damage, such as ordinary residential electrical systems can choose general chemical corrosion resistant wires. In addition, if the wires need to be used in occasions where they are frequently moved or bent, you can choose soft THIHN wires for easy bending. For example, the wiring of stage lighting equipment generally uses soft THHN wires. Hard THHN wires have high mechanical strength and are more suitable for fixed laying lines.

3. Specifications and dimensions of THHN Wire
|
Nominal cross section (AWG) |
Insulation thickness |
Nylon sheath thickness |
Nominal cross section (AWG) |
Insulation thickness |
Nylon sheath thickness |
|
18 |
0.38 |
0.10 |
9-5 |
0.76 |
0.13 |
|
16 |
0.38 |
0.10 |
4-2 |
1.02 |
0.15 |
|
14 |
0.38 |
0.10 |
1-4/0 |
1.27 |
0.18 |
|
12 |
0.38 |
0.10 |
213-500kcmil |
1.52 |
0.20 |
|
11-10 |
0.51 |
0.10 |
501-1000kcmil |
1.78 |
0.23 |
4. Main performance indicators of THHN Wire
|
Test Name |
Test requirements |
Test results |
Test standards |
|
Combustion test |
pass |
pass |
UL 1581 |
|
Water immersion insulation resistance test |
pass |
pass |
UL 1581 |
|
Winding and low temperature bending tests |
No cracking |
No cracking |
UL 1581 |
|
Oil resistance test |
pass |
pass |
UL 1581 |
5.Summarize
THHN cable and THWN cable have won the favor of many customers in the power and construction fields with their high heat-resistant nylon sheath layer and high-strength polyvinyl chloride (PVC material) insulation. The selection of cables is crucial to the efficiency, safety and long-term stability of power transmission. Therefore, this article introduces the structural characteristics of THHN and explains the usage scenarios. I hope it will be helpful to everyone! It is recommended to continue to pay attention to State Grid Cable for more information.


